Antibody Testing
Endocrinology Consultants Is Now Offering COVID-19 Antibody Testing
What Is SARS-CoV-2 & What Is COVID-19?
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the official name of the novel coronavirus that is currently causing a worldwide pandemic. COVID-19 is the official name of the respiratory disease caused by SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 is highly contagious and is transmitted through respiratory droplets and contact with contaminated surfaces.
More information about COVID-19 can be found at the Center for Disease Control and Prevention CDC website: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/index.html as well as on https://www.coronavirus.gov/.
What Is The Incubation Period For COVID-19?
Although several studies are still in progress, according to the March 10th, 2020 study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, the incubation period for COVID-19 as measured from publicly confirmed cases is as follows: median incubation period is 5 days.
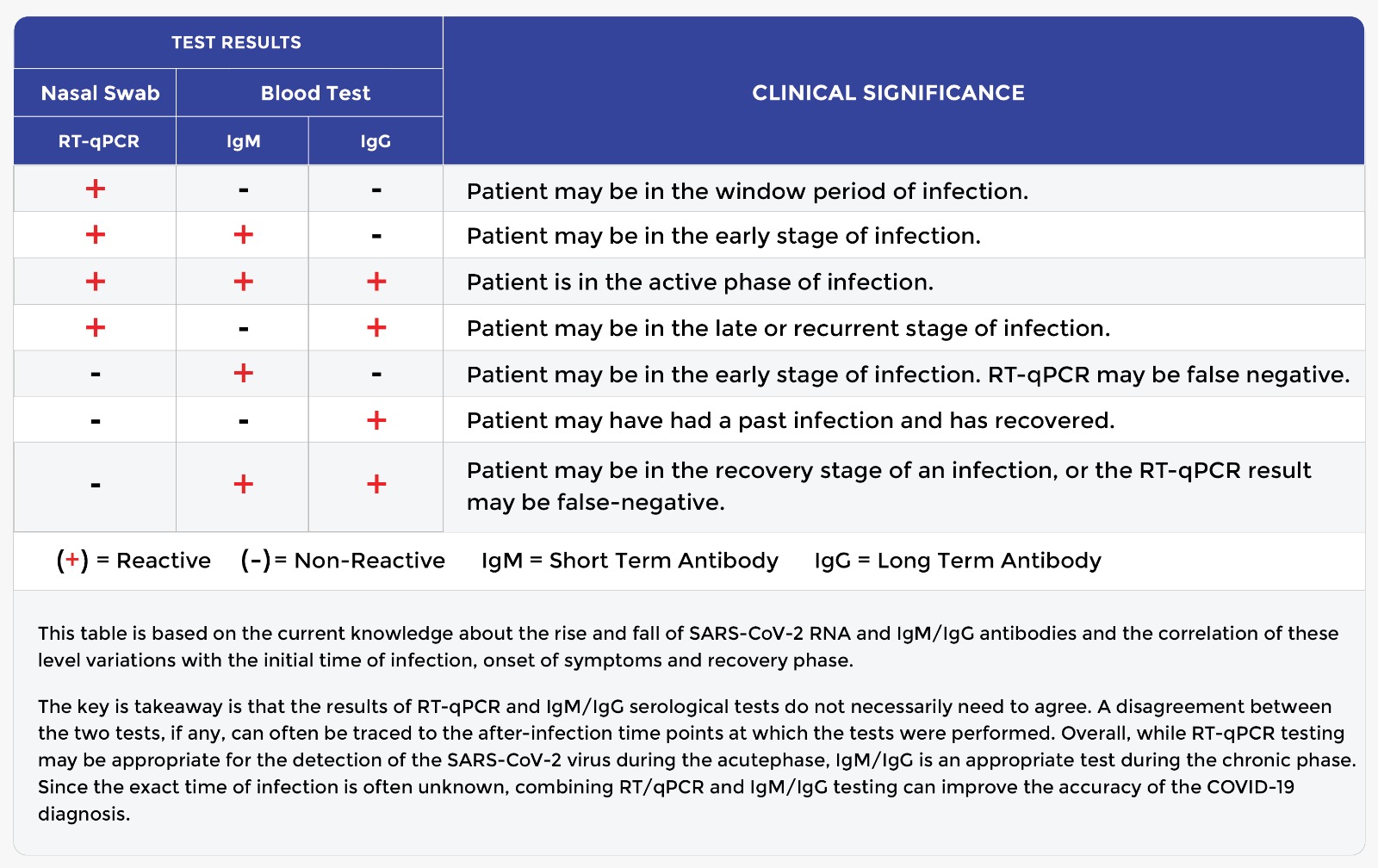
What is the COVID-19 Antibody Test?
The COVID-19 antibody test is a blood test that provides qualitative and quantitative detection of IgM and IgG antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 in individuals suspected of COVID-19. After infection, the virus antigen stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies that can be detected in the blood. Among these antibodies, the IgM antibodies appear early and are mostly positive after 3-5 days of onset.
The IgM titers then decrease while the IgG antibody potency starts to rise rapidly. During the recovery phase, the titer of the IgG antibody may increase four times or more compared to the acute phase.
Why the COVID-19 Antibody Test?
Combined with the Nasal Swab by RT-qPCR, the COVID-19 Serological Antibody Blood Test offers a valuable diagnostic tool in identifying infected patients. According to recent studies, the COVID-19 antibodies are not detectable before 3 days after onset of symptoms (or at least 7 to 10 days after infection). However, antibody tests can detect past infection because virus-specific antibodies can persist in the blood for several weeks/months after the onset of symptoms. Since the exact time of infection is often unknown, combining RT-qPCR (nasal swab) and IgM/IgG testing (blood test) can improve the accuracy of the COVID-19 diagnosis.
Who Can Be Tested?
COVID-19 Antibody Test is recommended to be used on patients with at least 5 days after onset of symptoms or 7-10 days after infection with the virus.
What Are The Guidelines On Testing People For COVID-19?
The CDC stated that “Clinicians should use their judgment to determine if a patient has signs and symptoms compatible with COVID-19 and whether the patient should be tested”. In addition, priority testing should be given to:
- Hospitalized patients who have signs and symptoms compatible with COVID-19 in order to inform decisions related to infection control.
- Other symptomatic individuals such as, older adults (age ≥ 65 years) and individuals with chronic medical conditions and/or an immunocompromised state that may put them at higher risk for poor outcomes (e.g., diabetes, heart disease, receiving immunosuppressive medications, chronic lung disease, chronic kidney disease).
- Any persons including healthcare personnel, who within 14 days of symptom onset had close contact with a suspect or laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patient, or who have a history of travel from affected geographic areas within 14 days of their symptom onset.
COVID-19 Antibody Test Limitations:
- For use in clinical laboratories by health care professionals following FDA guidance “Policy for Diagnostic Tests for Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) during the Public Health Emergency”.
- Negative results do not rule out SARS-CoV-2 infection, particularly in those who have been in contact with the virus. Follow-up testing with a molecular diagnostic assay (nasal swab) should be considered to rule out infection in these individuals.
- Results from antibody testing should not be used as the sole basis to diagnose or exclude SARS-CoV-2 infection or to inform infection status.
- Positive results may be due to past or present infection with non-SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus strains, such as coronavirus HKU1, NL63, OC43, or 229E.
- Not for the screening of donated blood.
